Why Doesn’t My Ethernet splitter work?? I figured it

Many users rely on an Ethernet splitter to optimize their home or office network, but when faced with the issue of an Ethernet splitter not working, their network setup may suddenly become inconvenient. Ethernet splitters are fantastic devices, leveraging the unused wires in a typical Ethernet cable to connect two devices through one cable. Hence, when they function correctly, Ethernet splitters are advantageous in managing clutter, extending the reach of a network, and saving costs.
However, navigating the intricacies of why an Ethernet splitter is not working could be a task. The precise cause can often stem from physical connection problems, compatibility issues, or interference. For instance, some users may find their Ethernet splitter not working with Cat6 cables, while others might find it not working consistently across all devices.
Tackling these problems requires a keen understanding of how an Ethernet splitter operates, its advantages, and its limitations. This ensures the troubleshooting process is effective and tailored to resolve specific problems. Undoubtedly, there are scenarios where the Ethernet splitter not working properly remains an issue despite troubleshooting, prompting users to consider replacement as a suitable solution.
Join us as we delve deeper into the world of Ethernet splitters, outlining various reasons and solutions when an Ethernet splitter not working, helping you restore an efficient and orderly network setup. We’ll help you understand, diagnose, and solve these Ethernet splitter problems from hardware issues to software complications.
What is an Ethernet Splitter?
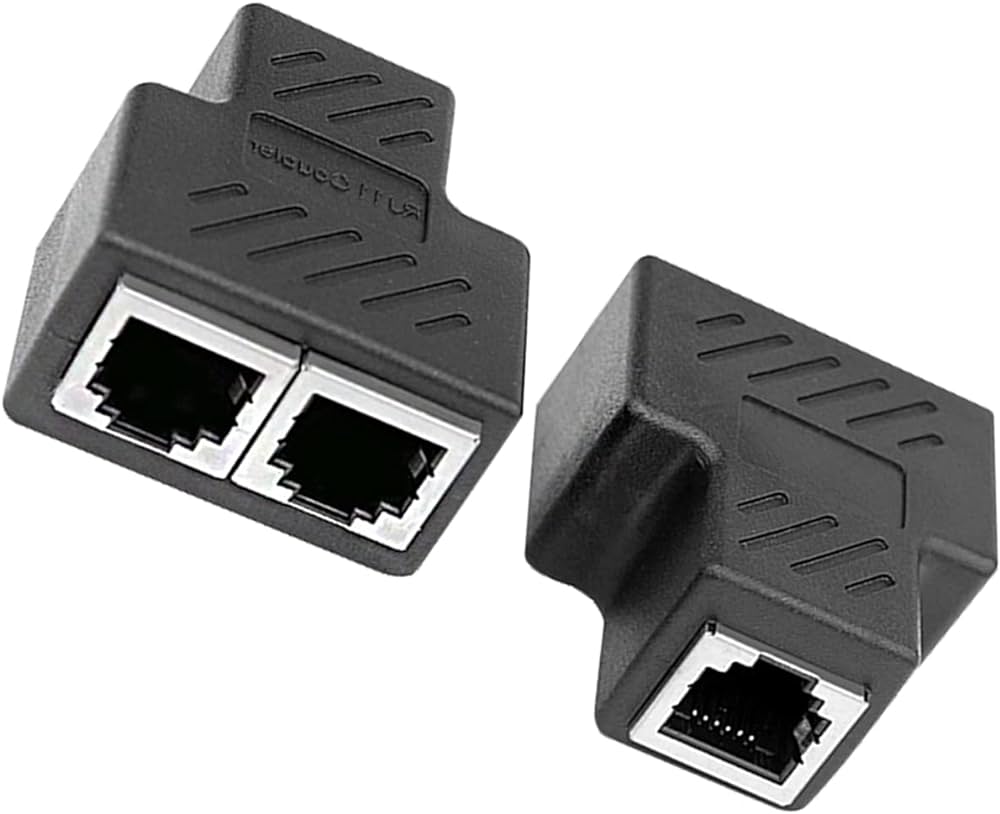

An Ethernet splitter is a small gadget that connects two devices into one Ethernet cable. Its main use is to limit the number of Ethernet cables running from your router or switch to your devices, reducing physical clutter and the cost of extra cabling.
The splitter operates because only four out of eight wires inside an Ethernet cable are needed to send and receive data. Essentially, the splitter combines two Ethernet connections into one single Ethernet cable, allowing two devices to use the same cable.
It’s worth noting that Ethernet splitters operate only at the 10/100 Mbps Ethernet standard, as this standard uses only four wires in a cable. The more modern Gigabit Ethernet (10/100/1000 Mbps) employs all eight wires for data transfer, making a splitter ineffective.
Ethernet splitters prove beneficial in specific situations, such as a home or small office setup, where cable management and cost are significant factors. However, for larger networks or when data speed is critical, a network switch would be a better solution due to its ability to work with higher data speeds and more devices simultaneously.
How Does an Ethernet Splitter Work?
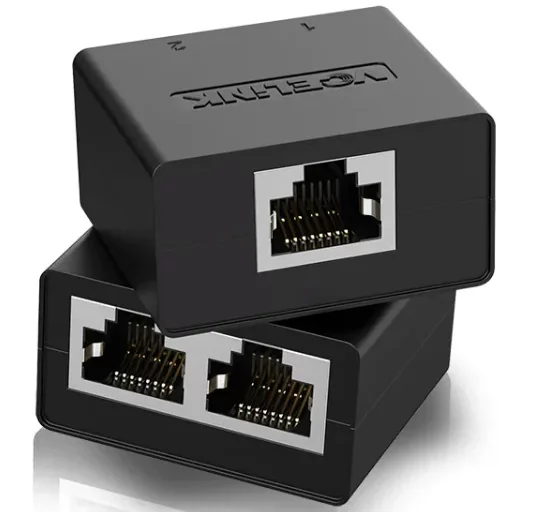

An Ethernet splitter works by taking advantage of the fact that most Ethernet cables only utilize four of the eight wires available for data transmission.
In a typical Ethernet cable, wires are paired, meaning data is sent and received over two wires. That leaves four of the eight wires unused. An Ethernet splitter takes advantage of this by using those unused wires to carry a secondary signal, effectively doubling the capacity of the Ethernet cable.
The splitter consists of two pieces, one at each end of the intended connection. At the originating end (let’s say near a router), the splitter takes two Ethernet cable inputs and combines them into a single output that could go, for instance, into a longer-run cable. That long-run cable now carries two sets of send/receive data—essentially two Ethernet connections—and ends at another splitter. This splitter at the destination site (for example, a room far from the router), separates the two signals back into its original two Ethernet cables, which can be plugged into two different devices.
This way, the splitter enables two devices to share a single cable without any signal loss or decrease in speed. However, this only works when both devices operate on a 10/100 Mbps Ethernet standard. Gigabit Ethernet, or 10/100/1000 Mbps, uses all eight wires for data transmission, which means a splitter won’t work in this scenario.
So, while an Ethernet splitter does not directly increase the network speed or bandwidth, it enables further efficient usage. Practically, an Ethernet splitter cuts the cost and reduces the clutter of extra cables but it does have its limitations with speed and compatibility.
It’s important to note that today, switch devices have widely replaced splitters, delivering enhanced functionality, including faster data speeds, more ports, reduced signal interference, and greater compatibility with various devices and network types.
What Are the Benefits of Using an Ethernet Splitter?
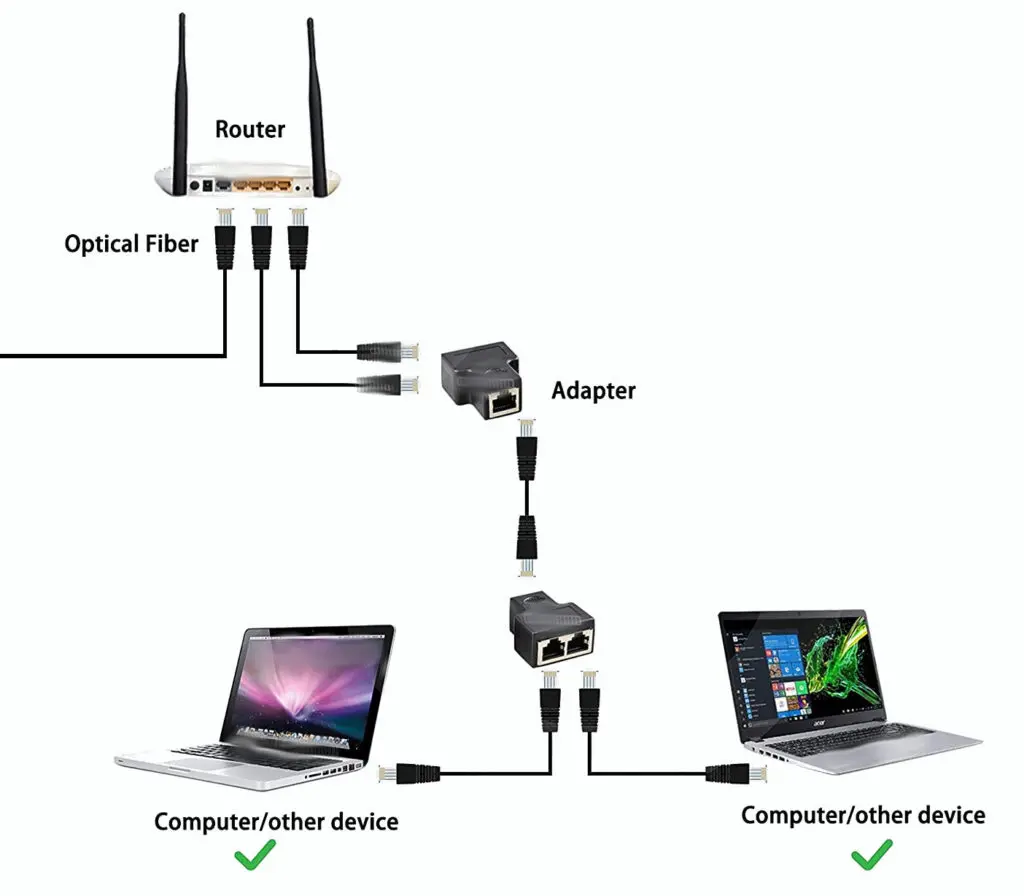
Using an Ethernet splitter offers several significant benefits:
1. Reduced Clutter: Ethernet splitters consolidate several cables into one, reducing clutter and making for a more organized and easier-to-manage network setup.
2. Cost-Efficient: A splitter can significantly decrease the cabling needed and lower networking costs by allowing multiple connections from a single Ethernet cable.
3. Extended Network Reach: In certain scenarios, Ethernet splitters can help extend the reach of a network. By minimizing the number of individual cables running from your router or switch, a splitter can enable you to connect devices located further away.
4. Maintains Speed: Ethernet splitters allow two devices to simultaneously benefit from a single Ethernet connection without leading to a decrease in network speed for either device. This is because Ethernet cables usually only use four of the eight internally available wires for data transfer, thus the extra four can be exploited for an additional connection without compromising data transmission speed.
5. Compatibility: Splitters are generally compatible with many types of Ethernet cables, including Cat5, Cat5e, and Cat6.
6. Ease of Installation and Use: Ethernet splitters are plug-and-play devices that don’t require special software or complex installation processes.
7. Counter Overcrowded Ports: An Ethernet splitter can effectively double the number of available ports when your router or switch doesn’t have enough Ethernet ports for all your devices.
Remember, Ethernet splitters do not necessarily boost network speed or increase the overall capacity of a network. They can, however, improve network efficiency and organization. Also, note that splitters work only with 10/100 Mbps network standards and won’t work with higher speed requirements like gigabit connections. For more advanced configurations, a network switch would be the preferred choice.
What Are the Limitations of Using an Ethernet Splitter?

While Ethernet splitters offer several notable advantages, they do come with a set of limitations:
1. Network Speed Restrictions: Ethernet splitters are designed to operate only with the 10/100 Mbps Ethernet standard. They use only four of the eight wires in an Ethernet cable to transmit data. On the other hand, Gigabit Ethernet (10/100/1000 Mbps) utilizes all eight wires, rendering splitters ineffective.
2. Limited Devices Connection: An Ethernet splitter can only divide an Ethernet cable into two connections. Attempting to connect more devices would require multiple splitters or a switch.
3. Incompatibility With POE: Power over Ethernet (POE) cannot be utilized with Ethernet splitters. POE requires all eight wires in the Ethernet cable, which conflicts with the initial design of splitters to utilize the spare four wires for an additional connection.
4. Potential Compatibility Issues: Cases in which an Ethernet splitter does not work with Cat6a cables or an Ethernet splitter does not work with VLANs, for example, highlight that they may not be compatible with certain types of networks or cables.
5. Inefficient for Large Networks: In larger network settings, the Ethernet splitter might not be efficient. More advanced networking hardware, like switches and hubs, would be more suitable for larger networks.
6. Quality Varies: There is a wide variety of splitters available on the market, with quality and performance varying significantly between them. Cheaper, lower-quality splitters often have issues with signal degradation or durability.
Understanding these limitations is essential before incorporating Ethernet splitters into your network setup. While adequately useful in specific situations, alternatives like switches may better suit certain scenarios, particularly for the gigabit network requirements or larger, more complex network environments.
Troubleshooting an Ethernet Splitter
If you’re facing problems with your Ethernet splitter, such as the Ethernet splitter not working properly or the Ethernet splitter not working with all devices, a detailed troubleshooting process can help diagnose and resolve the issue.
1. Check the physical connections: An incorrect or loose connection might cause the Ethernet splitter to malfunction. Check if the splitter is connected correctly and firmly to the Ethernet cables and devices.
2. Check Compatibility: Ensure that the Ethernet splitter is compatible with your network, devices, and Ethernet cables. In cases where the Ethernet splitter is not working with Cat6 cables or the Ethernet splitter not working with mesh networks, it might be a compatibility issue.
3. Try Using Different Ethernet Cables: Sometimes, issues arise from damaged or faulty cables. If an Ethernet splitter is not working with old cables, swapping them out might solve the problem.
4. Apply the Single Device Test: Try using the Ethernet splitter with a single device. If the Ethernet splitter is not working with multiple devices, the issue could be the splitter’s ability to handle numerous devices simultaneously.
Restart your Devices/Router/Switch: Sometimes, a simple device restart can solve many networking issues.
5. Update the Firmware: Outdated firmware might cause the Ethernet splitter not to work consistently. Ensure your router/switch and all devices run on the latest firmware versions.
6. Check for Network Interference: Electromagnetic interference (EMI), radio frequency interference (RFI), and other environmental factors can cause issues. If you suspect interference, you may need a shielded cable or consider moving your setup.
7. Use a Network Monitoring Tool: Network diagnostics tools like Ping, Traceroute, Wireshark, and PingPlotter can help identify latency, jitter, packet loss, and errors.
Fixing an Ethernet Splitter

If, after troubleshooting, your Ethernet splitter is still causing problems, the following solutions can be applied.
1. Replacement for Physical Damages: If the Ethernet splitter is physically damaged, it needs to be replaced. A split, bent, or exposed cable could affect the splitter’s performance.
2. Arranging a Compatible Setup: If compatibility is an issue, such as the Ethernet splitter not working with PoE++ devices or the Ethernet splitter not working with VLANs, using a different splitter or switch compatible with your network might be the solution.
3. Warranty Claim or Replacement: If the Ethernet splitter is defective, you may be able to get it replaced under the manufacturer’s warranty, assuming it is still valid.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q 1: What is an Ethernet Splitter?
A: An Ethernet splitter is a device that allows two devices to share a single Ethernet cable without sacrificing network speed. However, it’s important to note that it only works at 100 Mbps or less network speeds.
Q 2: Why is My Ethernet Splitter Not Working?
A: Your Ethernet splitter might not be working due to several reasons like improper or loose physical connections, compatibility issues with your device or network, use of damaged or faulty cables, or outdated firmware. In some instances, environmental factors like radio frequency or electromagnetic interference may also cause problems.
Q 3: Why is My Ethernet Splitter Not Working With Gigabit Speeds?
A: Ethernet splitters are meant to work with 100 Mbps or less network speeds. They do not support gigabit speeds. You should use a switch instead of a splitter if you need to connect multiple devices at gigabit speeds.
Q 4: Why is My Ethernet Splitter Not Working With My Cat6 Cable?
A: The splitter and the Cat6 cable could have a compatibility issue. Alternatively, the Cat6 cable may be faulty. Try using a different cable and ensure the splitter is compatible with Cat6 cables.
Q 5: Can I Use an Ethernet Splitter With Multiple Devices?
A: Yes, you can use an Ethernet splitter with multiple devices, but it may not always work optimally, depending upon the network capacity and the speed of your internet connection.
Q 6: What Should I Do if My Ethernet Splitter Doesn’t Work With Poe Devices?
A: Check the compatibility if your Ethernet splitter is not working with PoE devices. Some splitters may not support Power over Ethernet. In this case, a different splitter or PoE switch may be necessary.
Q 7: What Can I Do if My Ethernet Splitter is Physically Damaged?
A: If your Ethernet splitter is physically damaged, it’s recommended to replace it. A damaged splitter can lead to poor network performance or completely stop working.
Q 8: Does an Ethernet Splitter Reduce Internet Speed?
A: Technically, an Ethernet splitter doesn’t reduce internet speeds. However, if multiple devices access the internet simultaneously, the available bandwidth may be divided, potentially slowing the internet speed perceivable to each device.
Q 9: Can an Ethernet Splitter Work With Long Cables?
A: Yes, an Ethernet splitter can work with long cables. However, excessive cable length (more than 100 meters) can lead to degraded signal strength and slower network speeds.
Q 10: Does Updating the Firmware Help if an Ethernet Splitter is Not Working?
A: Yes, outdated firmware may cause an Ethernet splitter to work improperly. Regular updates can help keep the devices functioning optimally.
Conclusion
In conclusion, an Ethernet splitter is a useful tool, but it can face issues like any hardware. A systematic approach to troubleshooting can diagnose most problems. Regularly checking your physical connections, ensuring compatibility, using updated firmware, and performing routine network monitoring can help you avoid most problems. If your Ethernet splitter is damaged, opting for a replacement is the best course of action, possibly under warranty, if applicable. If compatibility is an issue, an alternate splitter or switch that fits your setup could solve the problem. Network tools and constant vigilance can help maintain the health and performance of your network and devices, thus ensuring a seamlessly functioning Ethernet splitter.